The Importance of Early Intervention for Autism
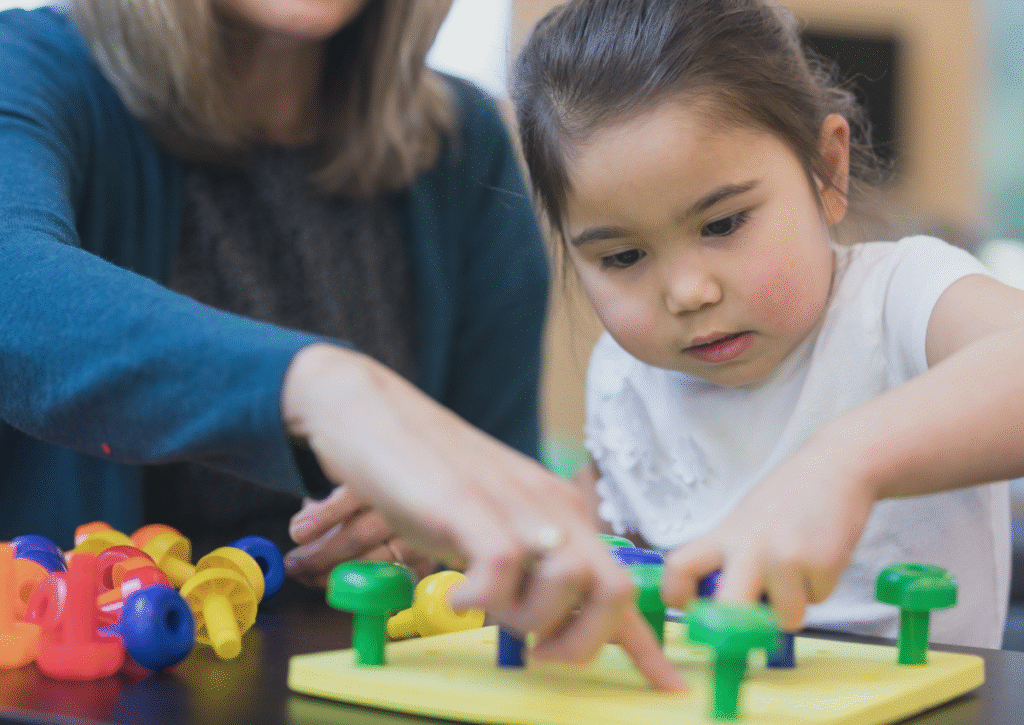

Over the past several years, we’ve seen a growing number of parents reaching out for services for their toddlers—often as young as 2 to 3 years old. This encouraging trend means families are pursuing evaluations and receiving autism diagnoses earlier than the national average. According to the CDC, the average age for an autism diagnosis […]
Top Gifts for Autistic Kids and Teens

Do you enjoy shopping for gifts for the holidays? Some relish the hunt for the “perfect gift”, while others stress over what to get their family and friends. And when you have a child or loved one on the autism spectrum, you may think finding a gift is even more challenging. However, it doesn’t have […]
Halloween and Autism: 6 Tips to Prepare Your Child
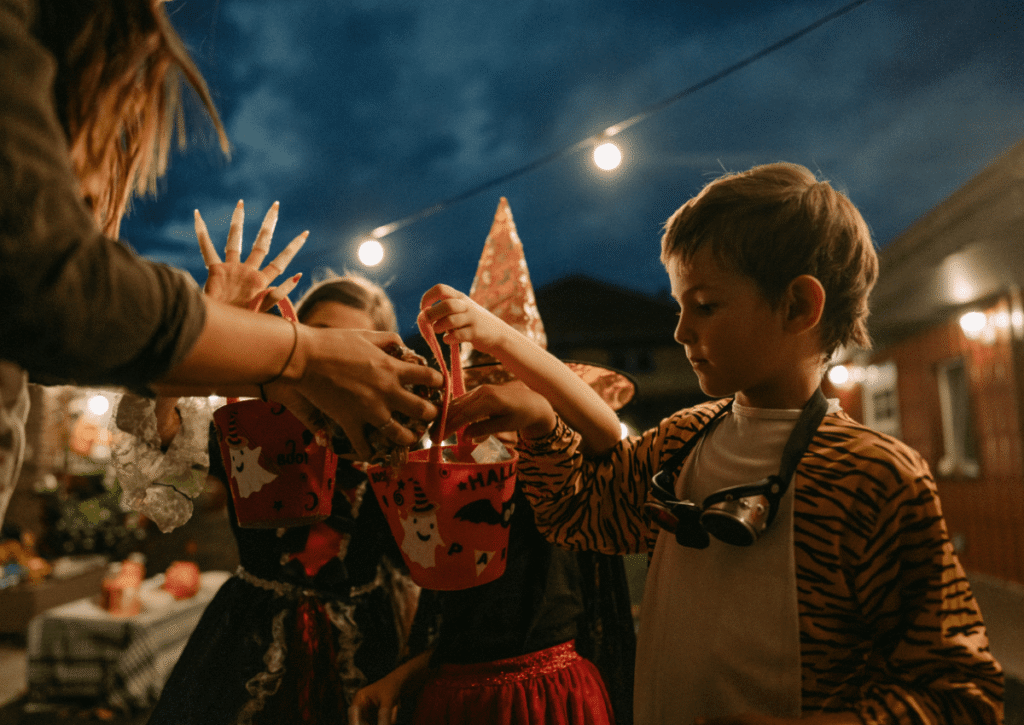

Halloween is a favorite for many kids–costumes, candy, and festive fun. But for children with autism, the unpredictability and sensory overload can make it challenging. At Healing Haven, we integrate holiday prep into therapy to help our clients enjoy the season. Here are six practical tips to help your child have a fun and stress-free […]
AAC: What It Is and Why It’s Important for Children with Autism
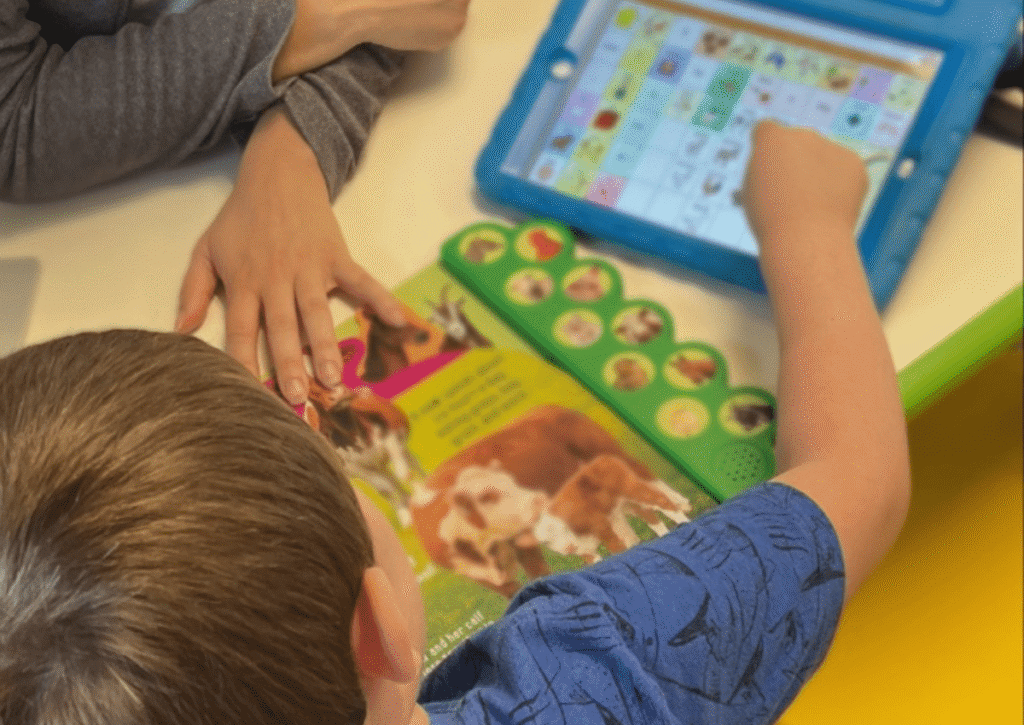

There are many means of communication used in our world. The most common ones used today are spoken words, gestures, eye gaze, facial expressions, print, sign language, and even GIFs. When it comes to individuals with speech and language delays, it is possible to augment and provide alternative options for them to efficiently communicate with […]
Healing Haven Clinton Township Clinic Open House
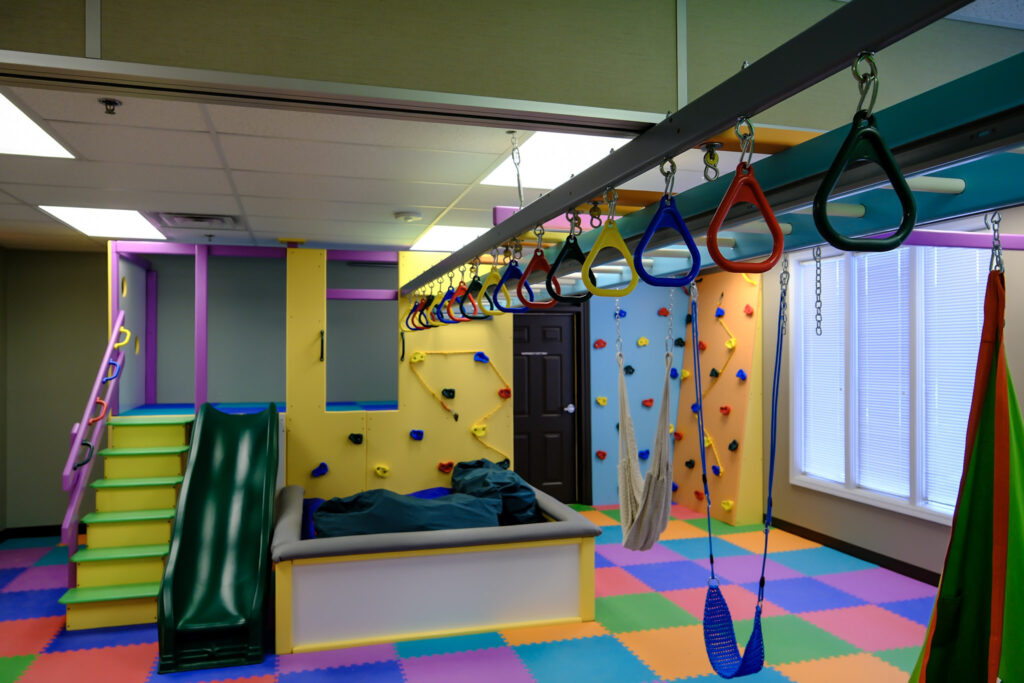

Exciting Expansion in Metro Detroit We have an exciting announcement! Our newest therapy clinic in Clinton Township is now open, marking our latest expansion into a new area of Metro Detroit. This impressive 19,000 square foot facility, which began welcoming clients in September, is specifically designed to serve children up to 12 years old. The […]
Developing School and Community Skills for Children with Autism

Helping Your Child Feel More Confident ABA therapy provides many benefits to children with autism in ways both big and small. Typically, this comes down to emphasizing skills that a child needs in two different settings. These settings are school and everyday life (also known as the “natural environment” in ABA). Everyday life includes home […]
Understanding Gestalt Language Processing and How it Impacts Your Child’s Communication

As speech-language sciences progress, many are learning about how speech processes correlate with how autistic adults and children communicate with others. A term that is becoming better understood in the speech-language community is Gestalt Language Processing (GLP), or Natural Language Acquisition. In turn, this term has become increasingly used in the autism community. You may […]
Fifteen Years Serving the Autism Community
It’s 2025 and we are celebrating our 15th Anniversary! That’s quite a milestone for those working in this field of autism therapy. We are proud of the unique blend of comprehensive autism therapy services we offer families. To celebrate, we are hosted a Family Fun Day Saturday, July 12. Let’s take a brief look back at our […]
Autism Acceptance and Finding Community

April is here again, which means it is time to celebrate and honor Autism Acceptance Month. Previously called Autism Awareness Month, the recognized period was started in 1972 by the Autism Society as National Autistic Children’s Week. It evolved from that into an entire month of recognition. In 2021, it was renamed from Autism Awareness […]
Developing Relationships on the Autism Spectrum

In the United States, our culture has predetermined ideas of what love “should” look like. As most of us have experienced, relationships can be complicated, autism or not. And developing relationships when you have autism is just as important as it is for those who don’t. Autism can cause differences in communication, understanding of context […]
