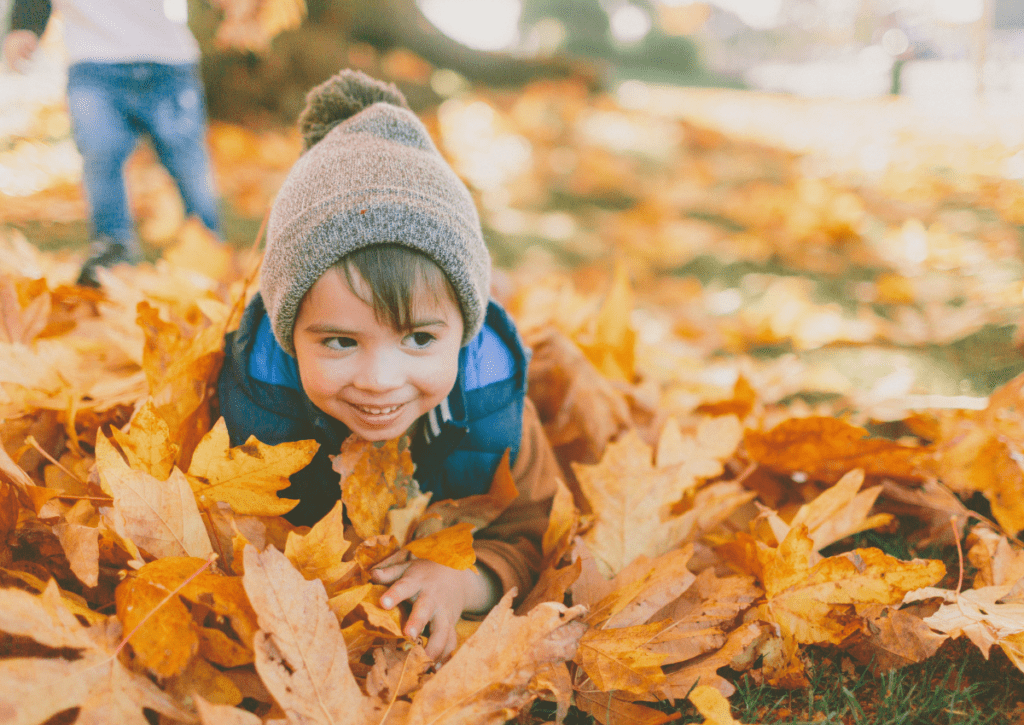
Fall has arrived! It’s time for cozy warm drinks, choosing Halloween costumes, and visiting pumpkin patches. Fall is also a season with lots of change as kids return to school and adjust to new schedules. With all these changes, it’s important to make time for some fun. And as you know, kids with autism often need sensory experiences to regulate well. Here are six DIY fall activities for kids with autism that are easy on the budget and engage the senses.
1. Sensory bin activities
Fill a small plastic bin with dried corn, chestnuts, pinecones, or any other dry fall goods. Kids with sensory needs are sure to love running their hands through the corn and feel the smooth or rough textures. Include items that help promote fine motor skill practice. This could be items like cups, spoons, or tweezers. Encourage your child to use these items to grab, scoop, and pour the colorful contents. Visit here for more sensory bin ideas.
2. Bake treats
Baking is a step-by-step process with a yummy result at the end. It’s a great activity for older kids working on following instructions and taking turns. Whip up pumpkin muffins, Halloween cut-out cookies, or a seasonal fruit crisp and see your child enjoy the tasty reinforcement of creating!
Fall is also the perfect time to roast some marshmallows over a fire. Enjoy time with your child outside in the crisp air, while helping them practice motor skills used to hold a marshmallow over a fire. Or, if being near an open flame with your child makes you nervous, you can alternatively use a grill or even the oven to get the marshmallows to the proper gooey state. The combination of different senses activated with this activity can be super stimulating for your child with autism.
3. Create fall-themed crafts
There are so many creative and fun fall-themed crafts you can experiment with to see what interests your child with autism. Two great options involve items that fall often brings an abundance of: apples and leaves!
If you’re tired of baking apples into pies and breads, or if you just have too many to eat, this season try utilizing them for a fun craft. Cut an apple in half, dip it into paint and press onto paper for cute, seasonal home-made stamps!
As for leaves, collect some of the many variations covering your yard and turn them into a sensory craft. Cover a fresh or dried leaf with a piece of paper and rub crayons or oil pastels over the paper. Consider using tracing or parchment paper and a light hand. While you do this activity, discuss with your child the unique shapes and patterns each leaf exposes through the paper. For more fall craft ideas, visit this list from The Everymom.
4. Make a corn squish bag
There are so many fall activities you can design with corn, but here’s a fun one for kids with autism who love squishy things. Fill a Ziploc bag with clear hair gel, corn kernels, and food coloring. You could also use permanent markers to draw a fall-themed design on the bag! Having your child assist with this activity can be a fun way to practice following directions and working together, especially if it yields a satisfying outcome for them.
5. Spend time outdoors
Here in Michigan, we are lucky to have a very profound change within seasons. Colors come out, leaves fall to the ground, and the air turns crisp around us. If you are fortunate enough to live here or somewhere else the change of seasons is evident and exciting, just being outdoors can be incredibly enjoyable for your child with autism.
Find a nearby trail, or even just take a walk through the neighborhood and enjoy observing and talking about the changes fall brings to the outdoors. Alternatively, you could spend some time in the yard helping your child create a leaf pile to jump into. The motor skills of collecting leaves by hand or rake combined with the sensory input of the texture, sound, and color of the leaves can create a lovely experience for you and your child to share.
6. Carve pumpkins
It’s a classic fall activity but carving pumpkins is full of sensory experiences, from feeling the smooth outside of the pumpkin to smelling (and feeling) the slimy, squishy seeds and membranes as you clean out the inside. You could even extend the activity by baking and tasting the pumpkin seeds or another pumpkin flavored treat! And as always, it’s fun for kids to choose a design, work with an adult to carve it, and then see the pumpkin light up with a candle inside.
Prepare for Halloween
In addition to all these fun fall activities for kids with autism, you may also want to start preparing them for Halloween. If this is their first time dressing up, going trick-or-treating, or they’ve struggled with these holiday traditions in the past, we have some ideas to help you prepare them. Head over to our blog post Halloween and Autism: 6 Tips to Prepare Your Child.
Autumn is filled with opportunities to add some sensory fun for your child and work on important skills in a fun way. Whether at home with these fall activities, or out in the community with cider mills, apple picking, pumpkin patches and hayrides, we’d love to hear your family’s favorite fall activities. Let us know in the comments!